1. FIRST-QUARTER GDP
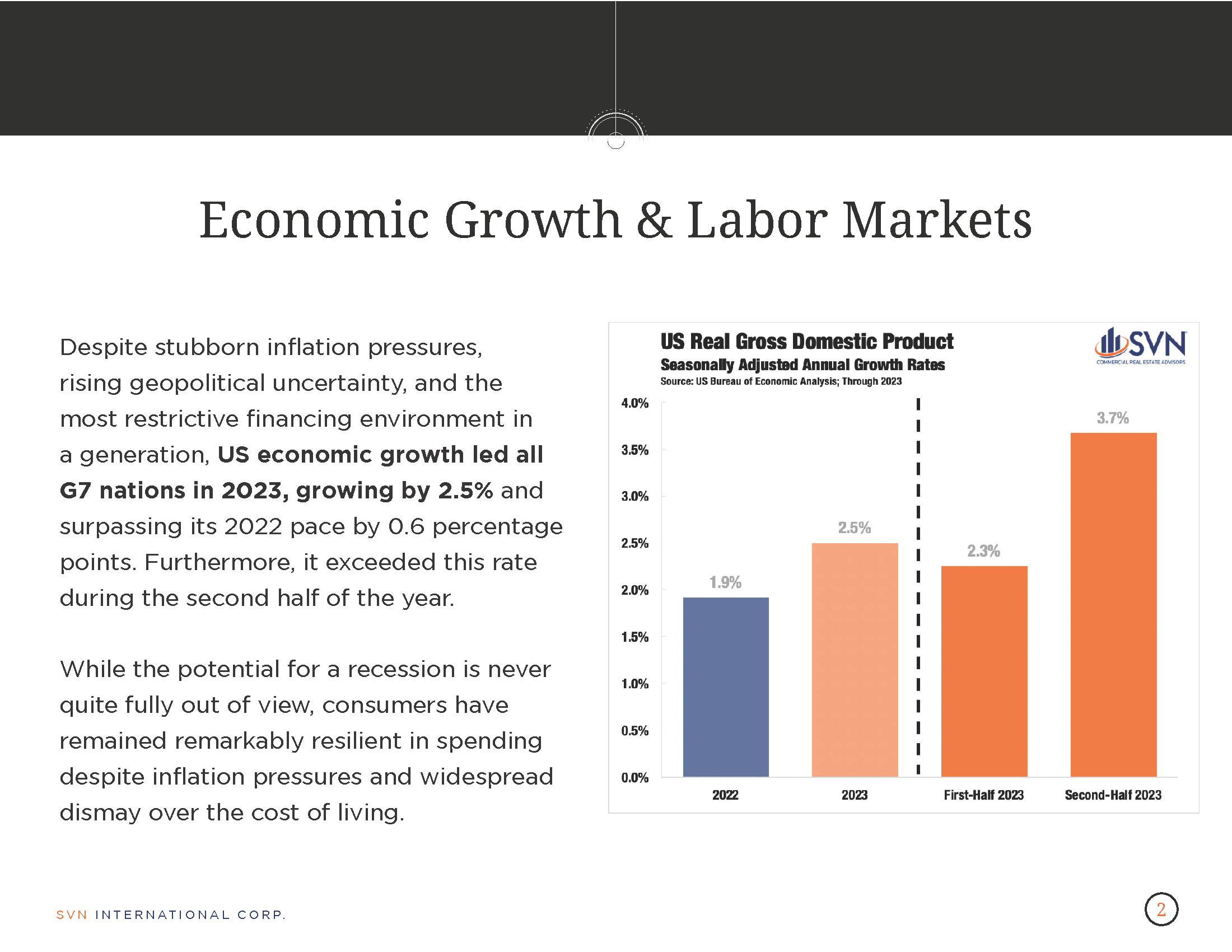
- The US economy expanded by a 1.6% annualized rate during the first quarter of 2023, according to the latest data from the US Bureau of Economic Analysis.
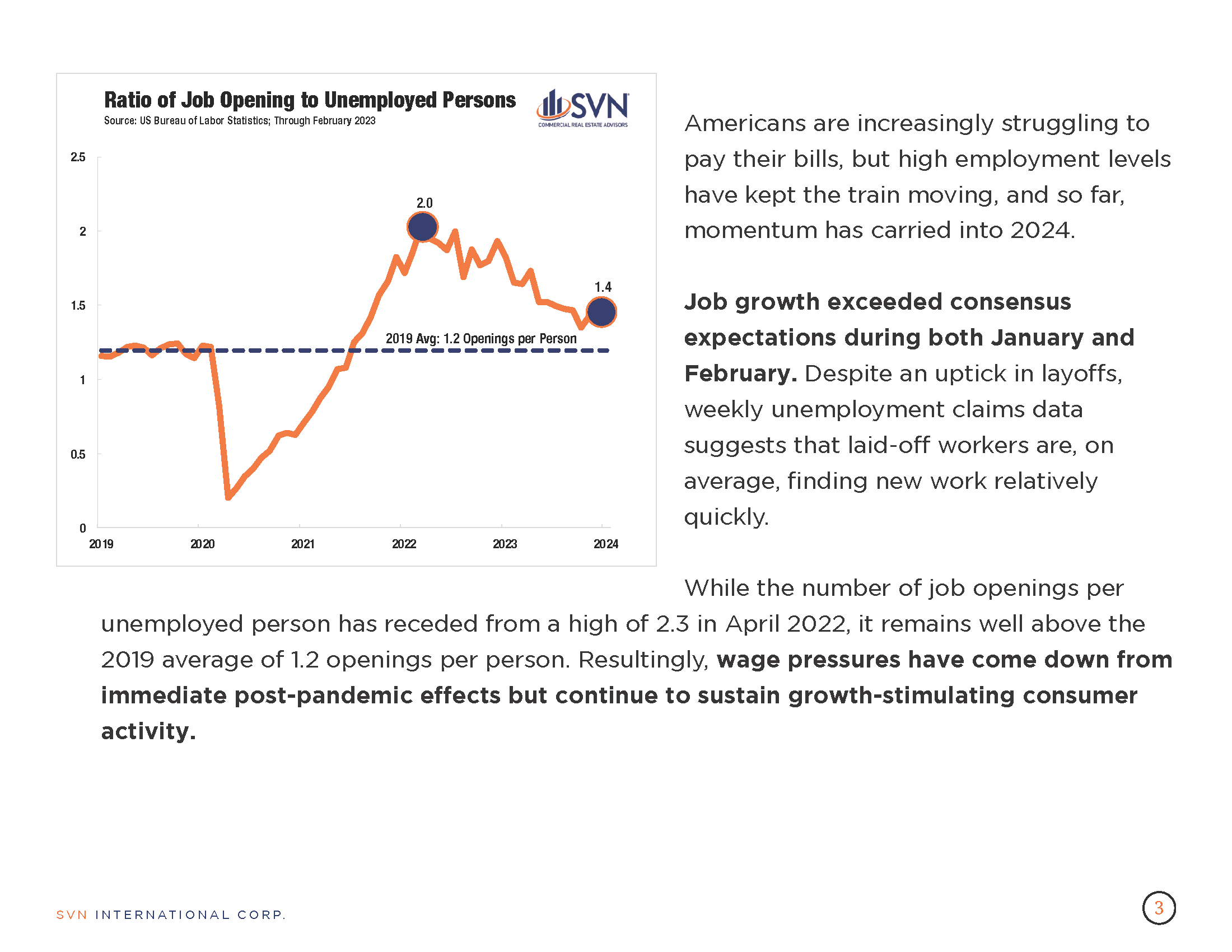
- First quarter GDP fell short of most estimates. Economists surveyed by Bloomberg, on average, forecasted a 2.5% pace of growth during the quarter.
- Q1 2024 was the second consecutive quarter where economic output slowed. It was also the lowest pace of growth since the economy contracted in the first half of 2024.
- Consumer spending slowed to an annual pace of 2.5% compared to 3.3% during Q4 2023. The downtick was mainly due to a fall in goods consumption while spending on services accelerated.
- Interestingly, the slowdown in consumption defies an uptick in price pressures evident in the March CPI release and challenges the reliability of recent inflation metrics. A central theory to this inconsistency is that inflation metrics’ use of “owners’ equivalent rent” as a proxy for rental costs distorts their shelter components, potentially resulting in overestimating price increases.
- Non-residential investment eased during the first quarter, but residential investment jumped tremendously, climbing from 2.8% during Q4 2023 to 13.9% in the latest reading.
- Government spending decelerated from an annualized 4.6% to 1.2%. Exports slowed sharply while imports soared. Meanwhile, private inventories continued to contract.
2. COMMERCIAL REAL ESTATE PRICES
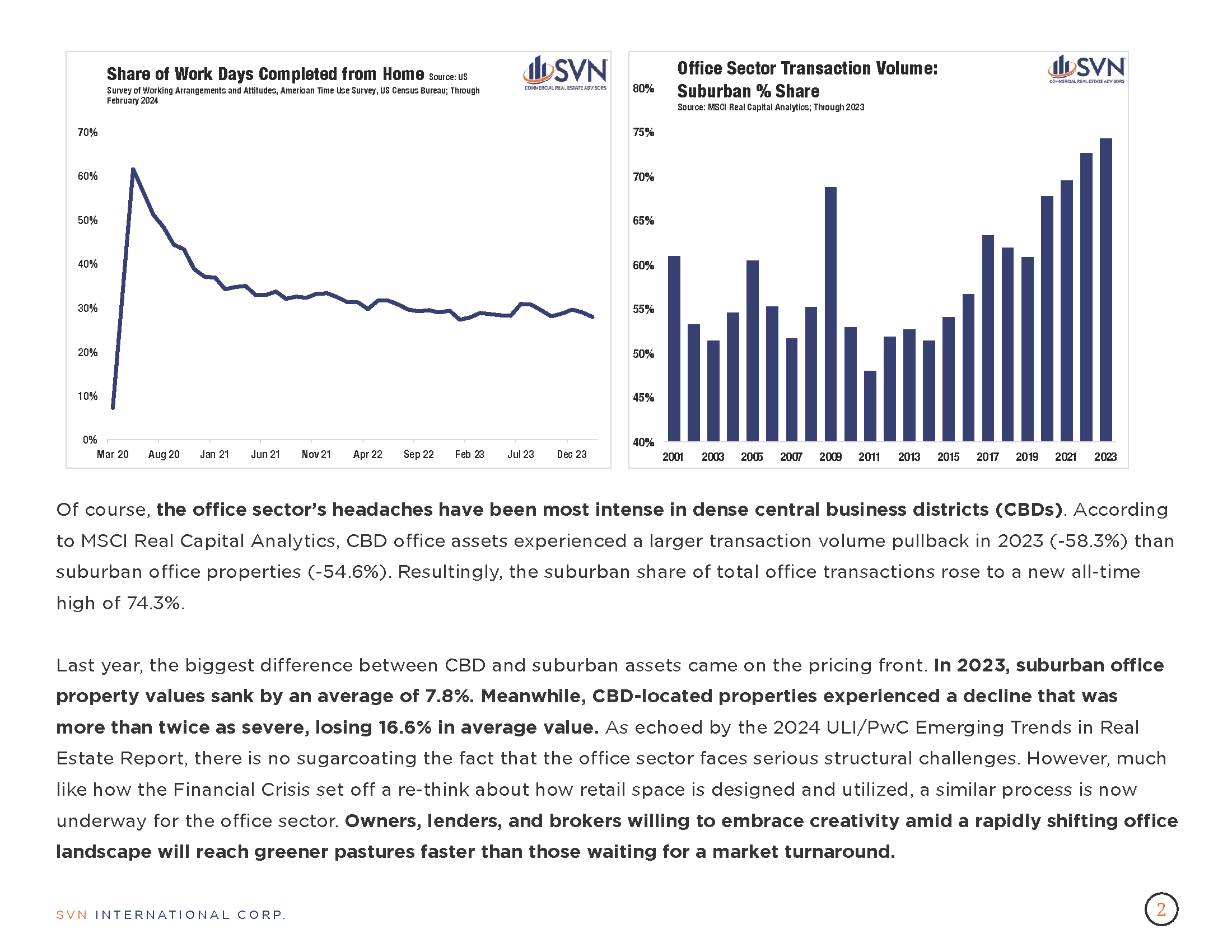
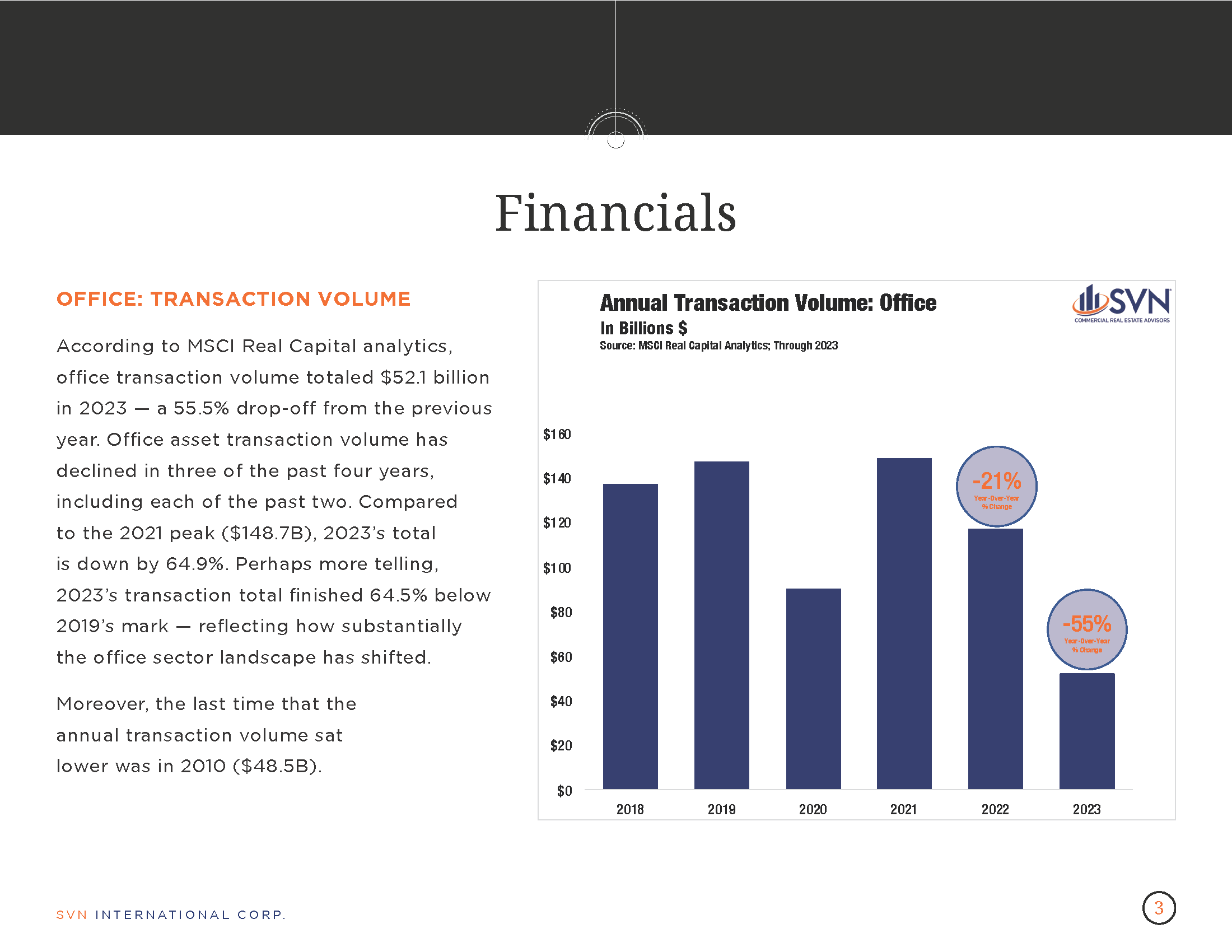
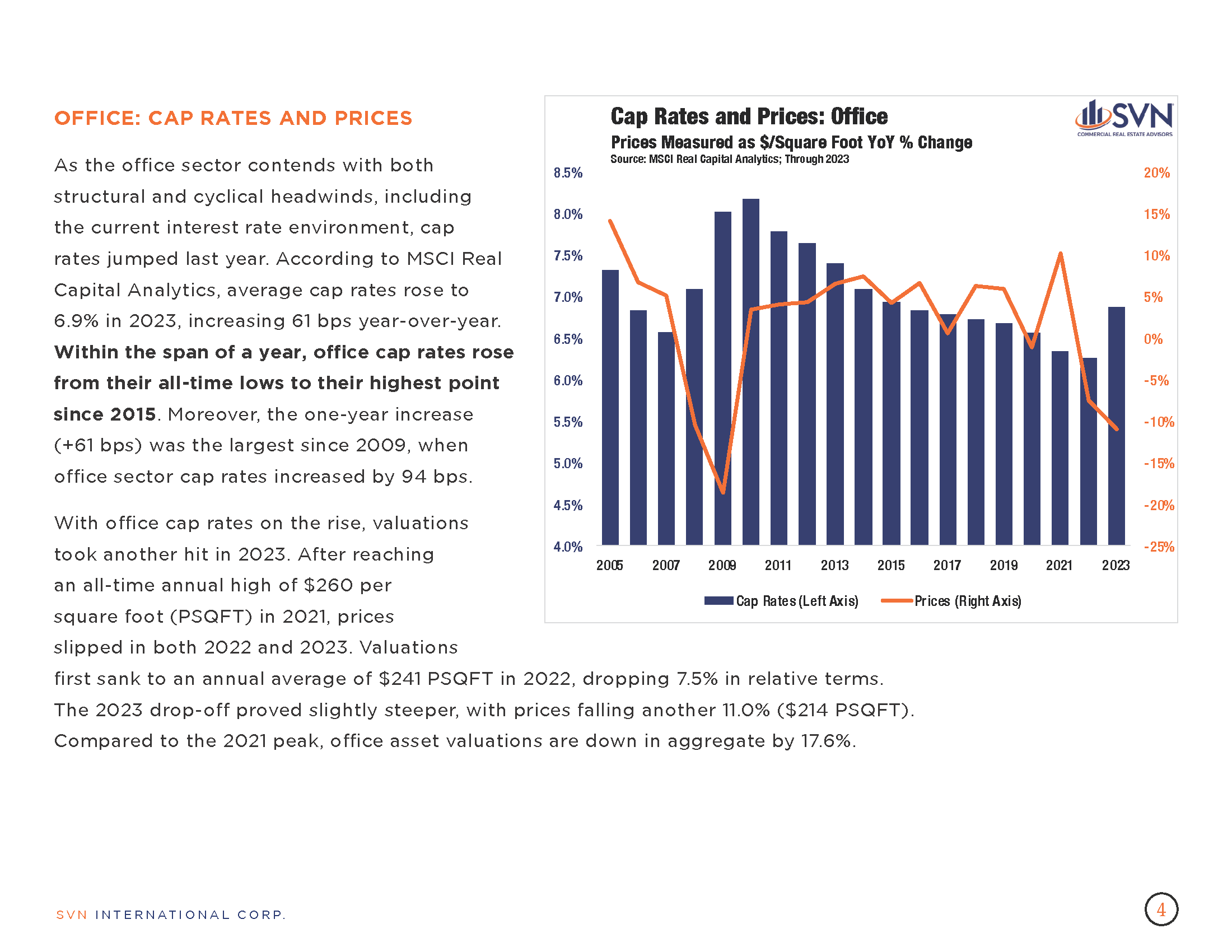
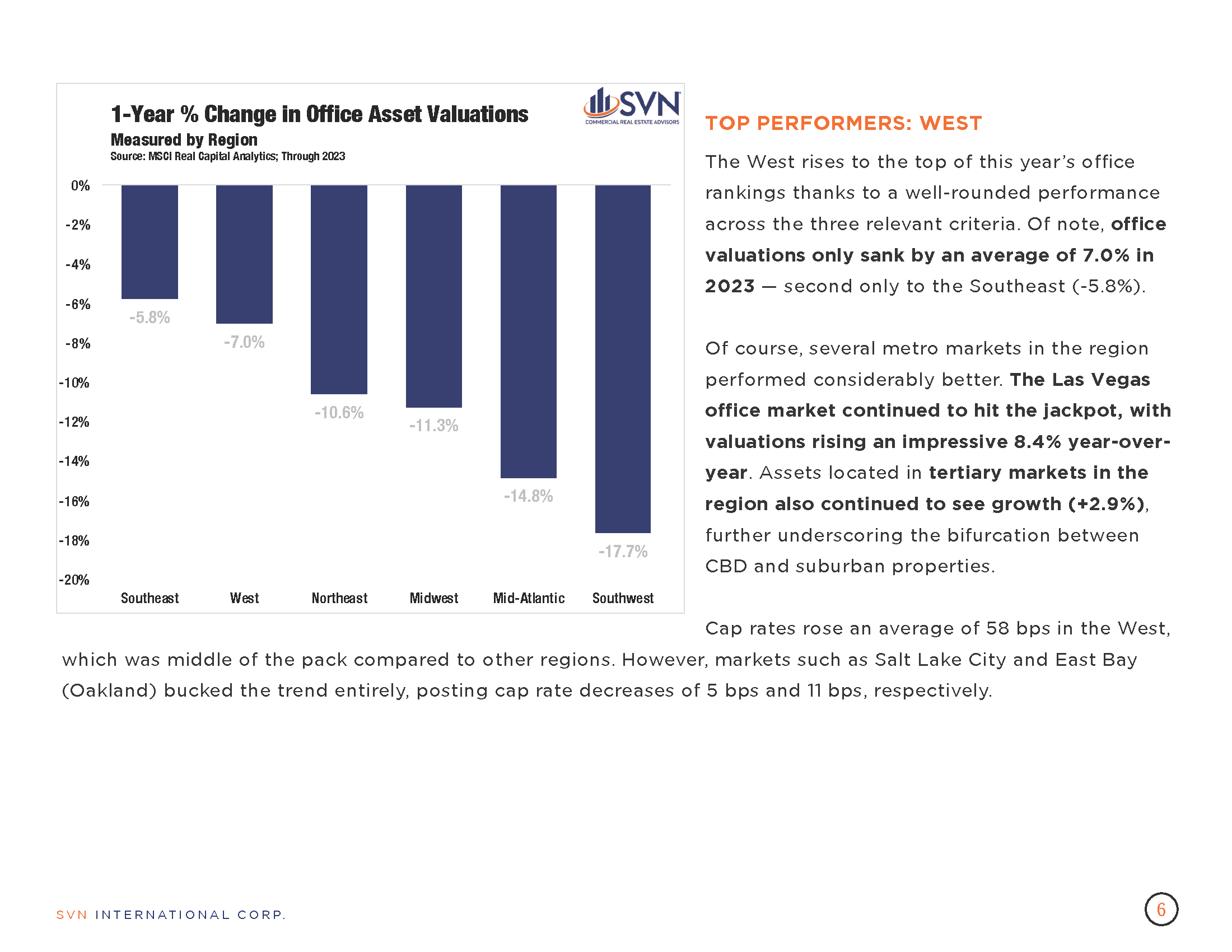
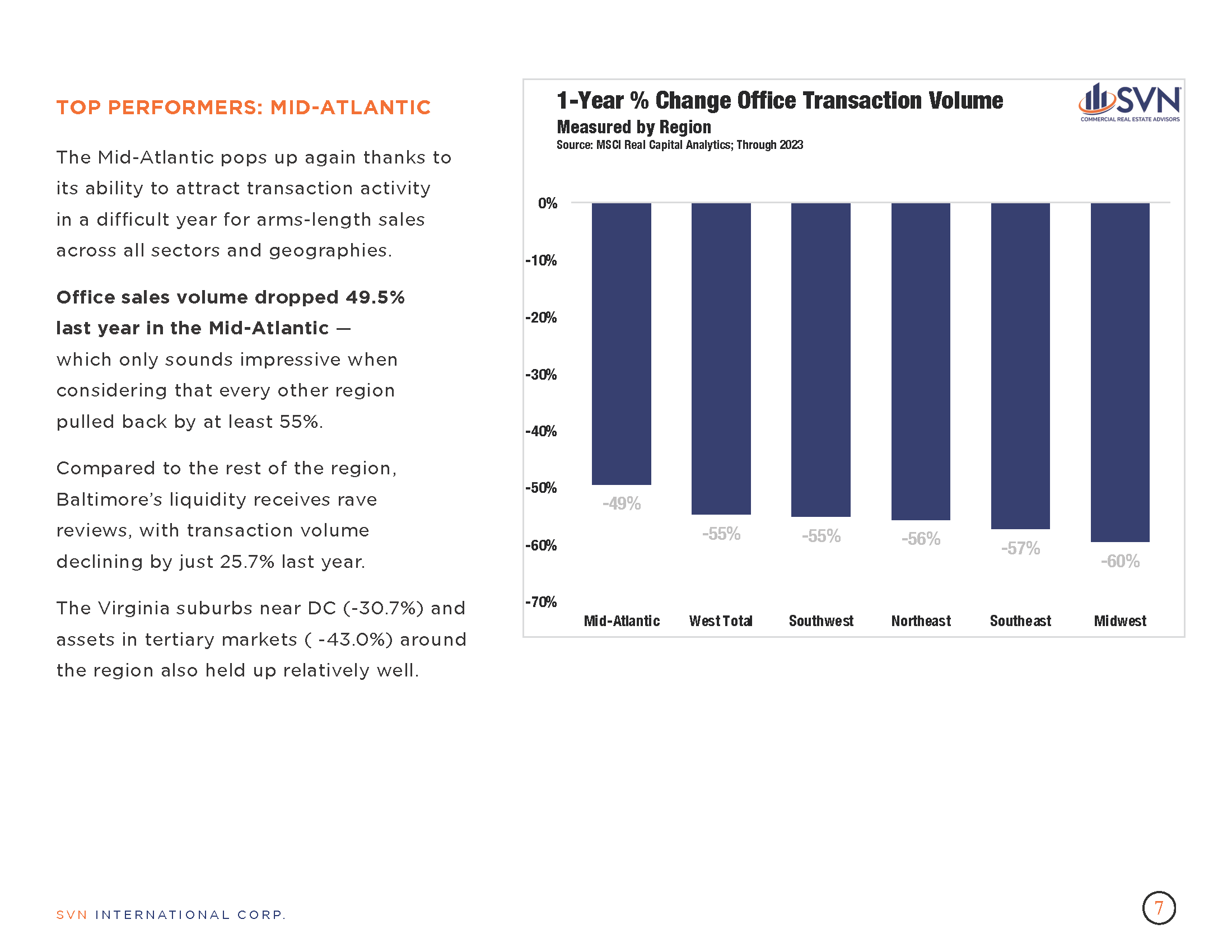
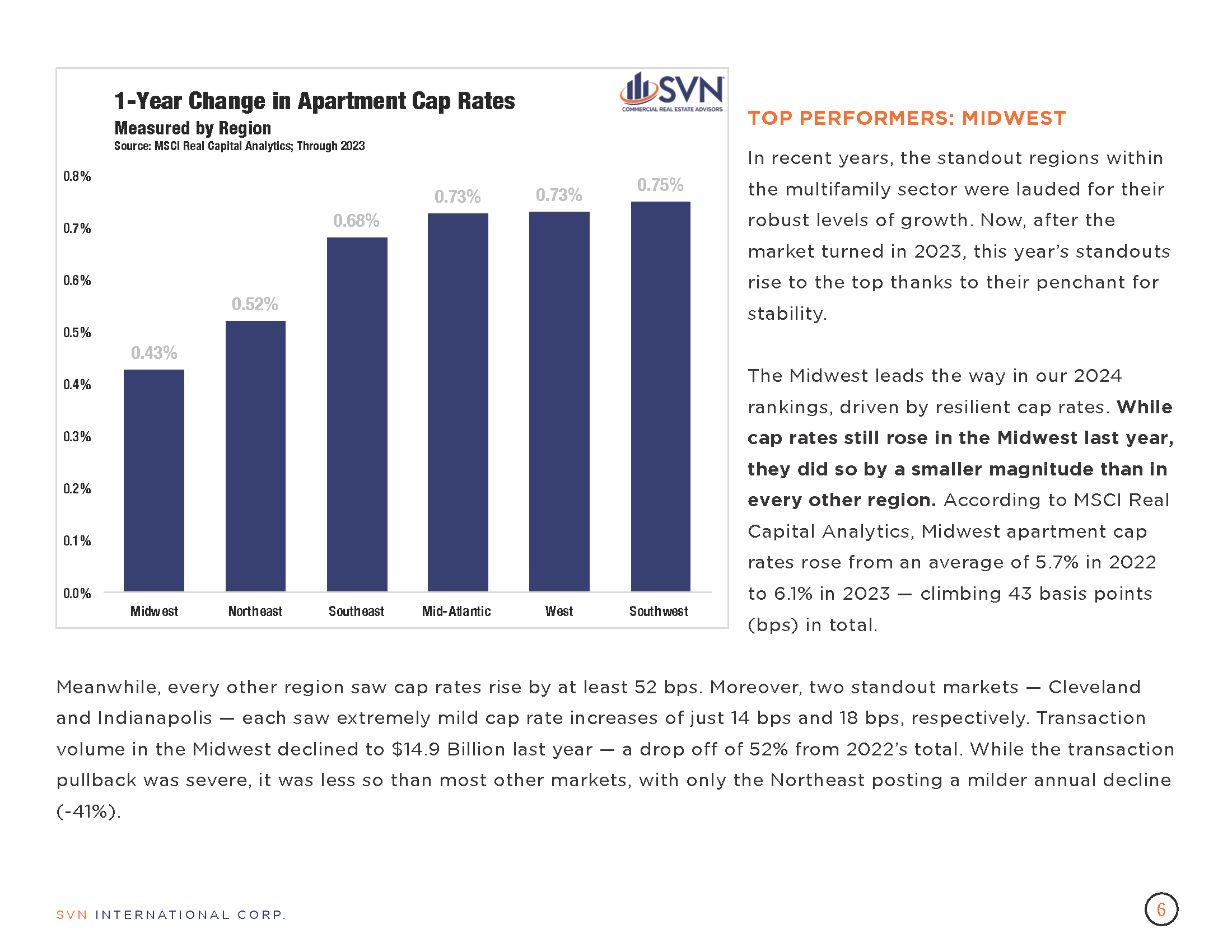
- According to the MSCI-RCA commercial property price index (CPPI), the pace of decline in US commercial sector prices slowed for the eighth month in March.
- Prices fell 3.0% year-over-year through March and just 0.2% from February.
- The industrial sector again arose as the only property type with an annual increase in March. The average price on an Industrial property climbed 0.7% month-over-month from February and 5.7% over the past 12 months. Annualizing the Industrial sector’s growth in March would bring the sector to a 9.2% increase over the next year.
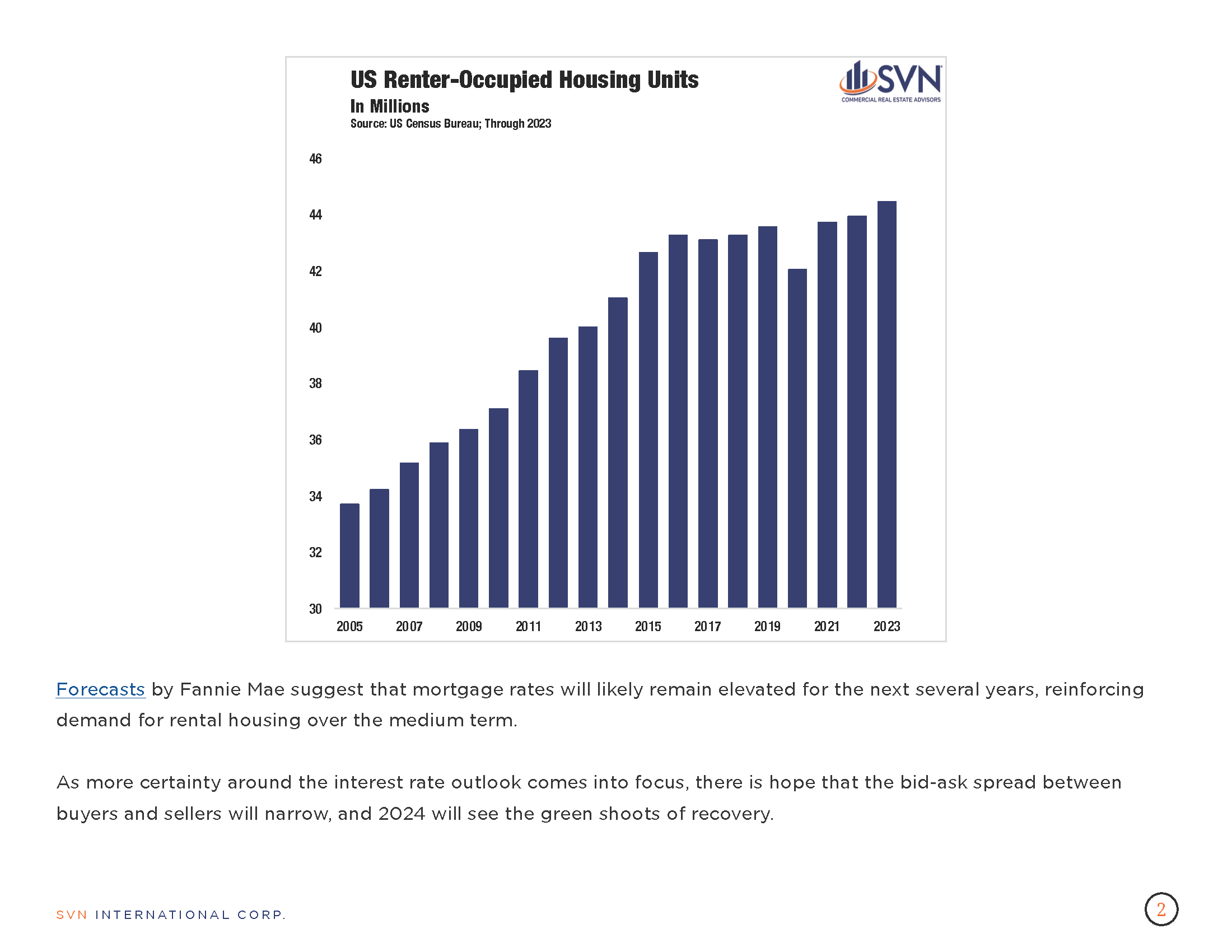
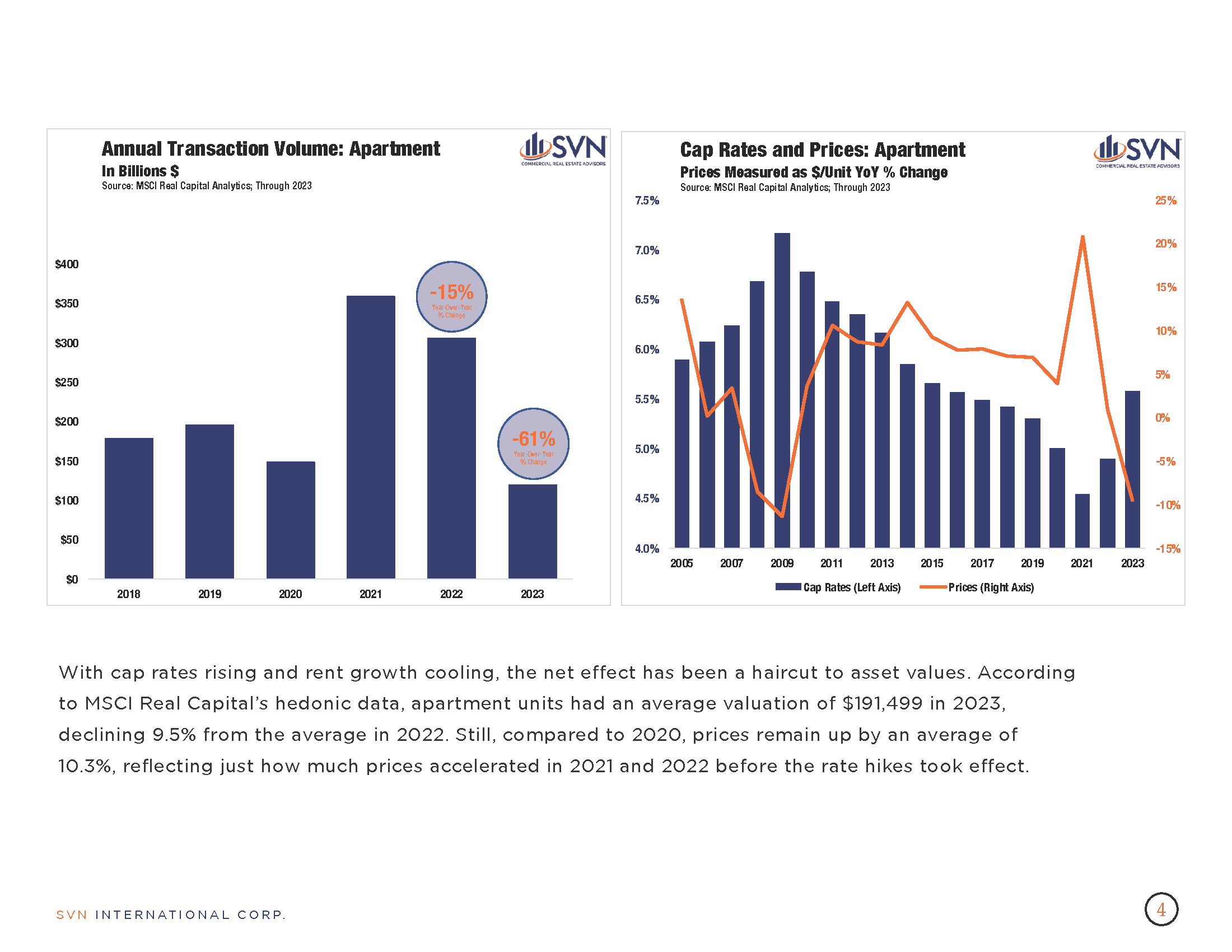
- The pace of decline for Apartment sector prices has slowed in each of the last seven months, with prices charting an 8.4% year-over-year decrease in March. On a monthly basis, the Apartment price index has declined for 20 consecutive months. Still, the sector is up 11.0% above its pre-pandemic level.
- Retail sector prices also improved. The sector’s annual price decline narrowed for the eighth straight month to 1.2% in March. Retail also joined Industrial as the only sector that saw prices climb monthly, climbing 0.1% from February.
- CBD office prices continue to fall more steeply than their suburban counterparts, falling 33.2% year-over-year compared to just 11.4%.
3. DOWNTOWN RECOVERY TRENDS
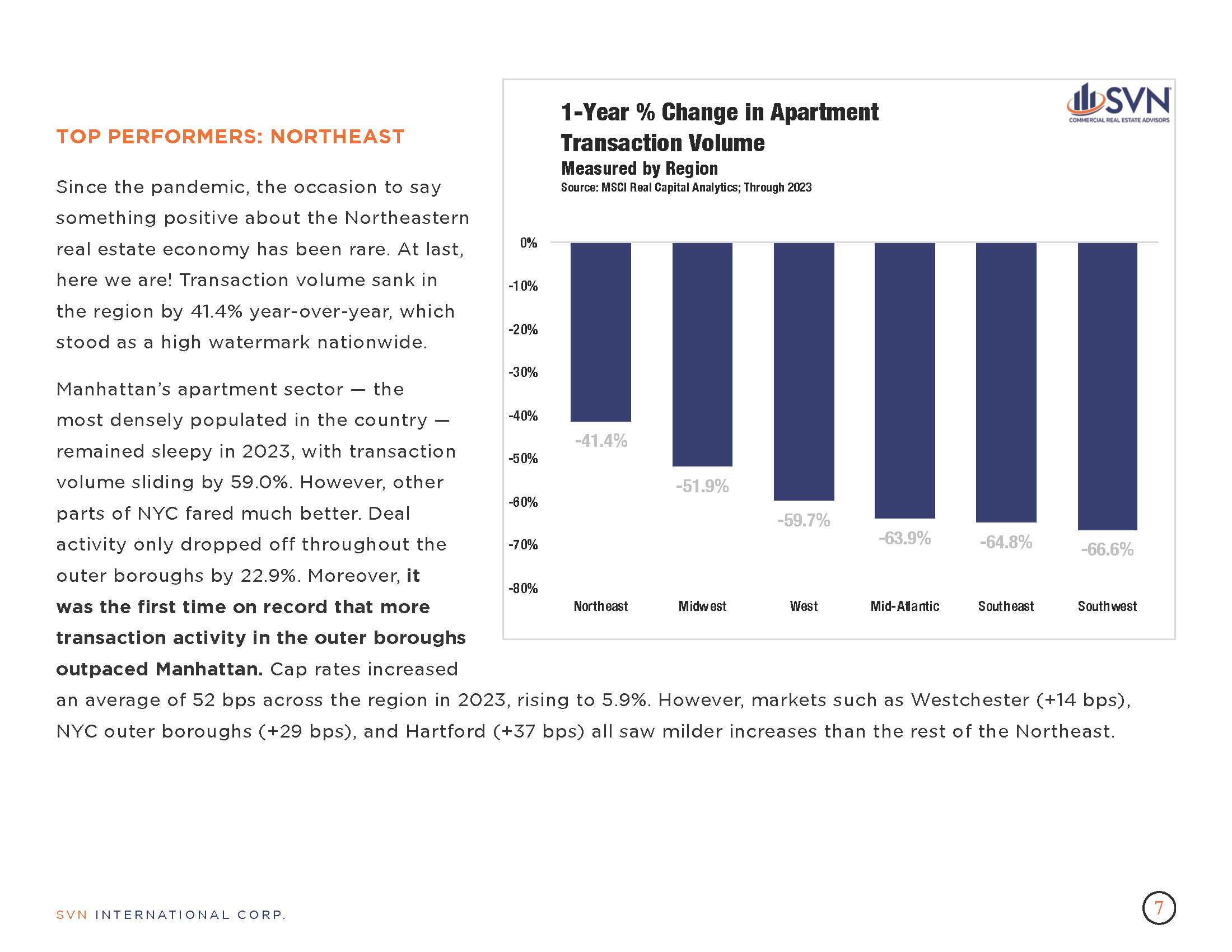
- Cell phone activity data tracked by the University of Toronto School of Cities show that between March 2023 and March 2024, downtown US and Canadian cities saw a median increase of 9.3% in foot traffic.
- While the findings do not detail the type of places where new activity occurs, they suggest that most downtown areas continue to gradually recover from the pandemic.
- Of the metros tracked, 50 cities have downtown areas experiencing a recovery compared to 14 that are trending downward.
- Notably, the report points out that among the metros trending downward are cities that had previously topped their rankings, suggesting that many of them recovered more quickly.
- The top five metro areas by year-over-year downtown activity growth were Minneapolis (+45.7%), Ottawa (+39.5%), Montreal (+38.6%), Chicago (+36.6%), and Louisville (+31.9%).
4. FED’S BEIGE BOOK SUMMARY
- According to the Federal Reserve’s latest Beige Book, nationwide economic activity has expanded slightly over the past six weeks. Still, performance has varied by region. 10 of 12 districts reported slight or modest increases in economic growth, up from 8 in the last round of reporting. Still, mixed sales activity across the 12 Fed districts meant that overall, consumer spending saw only a slight increase in consumer spending.
- Several districts reported declining discretionary spending as consumers remain increasingly price-sensitive to several goods categories. Some districts saw auto sales rise as inventories improved and dealerships wooed buyers with new discounts and incentives. Others saw modest increases in tourism as the spring season began, but reports vary.
- Commercial real estate leasing fell slightly, while non-residential construction was essentially flat. The most positive CRE sentiment came from the Minneapolis Fed district, where construction activity improved slightly.
5. CRE OUTLOOK IMPROVING, SAYS DOUBLE LINE
- A new research paper by DoubleLine suggests that a 2024 pivot in the Federal Reserve’s interest rate policy will open the door for price discovery and improve the market’s stability generally.
- As the interest-rate outlook becomes clearer, commercial real estate transaction activity should pick up, and market pricing will become more transparent. The report suggests that these mechanisms will allow for improved credit access and unlock existing demand.
- Roughly $2.8 trillion of CRE debt will mature between 2024 and 2028, making price discovery crucial as lenders seek market share.
- The paper expects payoff outcomes to persist among multifamily, industrial, and lodging while larger office loans and struggling mall properties may face additional refinancing difficulty.
6. NMHC APARTMENT INDEX
- According to the latest quarterly release of the NMHC Apartment Index, while rent growth in the Multifamily sector has slowed in recent quarters, sales volume has increased, and the equity financing environment has become more favorable.
- The first quarter of 2024 was the first time in two years that the Multifamily sector saw higher deal flow than the previous quarter. 21% of respondents surveyed by NMHC reported higher sales than just 6% during the final quarter of 2023.
- Equity financing improved marginally, but 60% of respondents found that availability was unchanged. Meanwhile, the debt financing environment has become tighter, with the Fed’s decision to push back potential rate cuts noted as a primary culprit.
7. FIVE APARTMENT MARKETS WHERE RENTS HAVE ROOM TO GROW
- According to a recent Chandan Economics analysis of Zillow data, as a home price rally during the pandemic spurred massive rent growth across the nation, some markets have seen home prices grow more quickly than rents. The gap suggests several of these rental markets have room for growth in the years ahead.
- McAllen, TX; Charlotte, NC; Durham, NC; Raleigh, NC; and Seattle, WA were identified as the top five metros for rent growth opportunities. Each metro has experienced a 20% or more difference between the growth rates of its home values and observed rents over the past four years.
- Since 1985, rents and home prices across the 100 largest US metros have had a 96% correlation. Cyclical factors such as those experienced during the pandemic can distort such longer-term structural relationships, suggesting that several of these markets may close the gap over time.
8. RATE UNCERTAINTY TAMES HOMEBUILDING MOMENTUM
- According to the latest data from the NAHB/Wells Fargo Housing Market Index (HMI), homebuilding held steady during April. Still, it ended four consecutive months of increases as interest-rate uncertainty dampens new activity.
- The components measuring current sales conditions and the traffic of prospective buyers each increased, albeit slightly. Meanwhile, sales expectations for the next six months fell somewhat.
- The report suggests that April’s flat reading indicates that homebuilding demand is present but in a holding pattern as would-be buyers asses the interest-rate outlook. As the potential for rate cuts in 2024 becomes clearer, pent-up demand may continue to materialize.
9. CRE FORECLOSURES JUMP
- According to data from ATTOM, foreclosure filings rose by 117% year-over-year through March 2024, with roughly 625 CRE foreclosures in just the past month.
- Foreclosures are up 6% from February. The figure considers commercial properties with at least one filing of a default notice, scheduled auctions, or bank repos.
- Foreclosures have risen steadily since May 2020, when, for context, they hit a record low of 141 properties during that month.
- California had the highest concentration of foreclosures during March, with 187, accounting for almost 30% of all foreclosures during the month. The Golden State has had an astonishing 405% year-over-year jump in CRE foreclosures.
10. PCE PRICE INDEX
- According to the latest data from the US Bureau of Economic Analysis, the PCE price index experienced its largest annual increase in four months. However, core prices (mirroring February’s rate) repeated their slowest rise in three years.
- The headline PCE price index rose 2.7% year-over-year, up from 2.5% in February.
- However, the core-PCE price index, the Federal Reserve’s preferred inflation metric when considering monetary policy, rose by a steeper 2.8% year-over-year in March. Alongside a similar uptick in February, it is the slowest increase for core prices since March 2021.
- The latest PCE data caps a complex month of data releases. Recent job growth and consumer prices rose higher than expected while consumer spending and the prices of those expenditures slowed.
SUMMARY OF SOURCES
- (1) https://www.bea.gov/news/2024/gross-domestic-product-first-quarter-2024-advance-estimate
- (2) https://info.msci.com/l/36252/2024-02-21/y1htr4/36252/1708559067qvvmBG37/2402_RCACPPI_US.pdf
- (3) https://downtownrecovery.com/charts/trends?utm_source=newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=newsletter_axioswhatsnext&stream=science
- (4) https://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/beigebook202404-summary.htm
- (5) https://doubleline.com/wp-content/uploads/DoubleLine-Commercial-Real-Estate-Update_2-6-24.pdf\
- (6) https://www.nmhc.org/research-insight/quarterly-survey/2024/nmhc-quarterly-survey-of-apartment-conditions-april-2024/
- (7) https://www.chandan.com/post/five-apartment-markets-where-rents-have-room-to-grow
- (8) https://www.nahb.org/news-and-economics/housing-economics/indices/housing-market-index
- (9) https://www.attomdata.com/data/foreclosure-data/
- (10) https://www.bea.gov/data/personal-consumption-expenditures-price-index#:~:text=A%20measure%20of%20the%20prices,reflecting%20changes%20in%20consumer%20behavior.





Danielle has more than 25 years’ experience specializing in real estate and property management with a focus on commercial, multi-family, residential property management, sales, and investments. As a native to Southern California, over the course of her career, Danielle has worked in various real estate markets with extensive leasing experience and local knowledge of residential market rates in cities throughout Los Angeles County and Orange County. Her skills and experience have led her to successfully manage and enhance the value of a portfolio by combining up to the minute core market knowledge, masterful negotiation skills, real estate transaction and business expertise, asset management, tactical goal setting, and solid real estate opportunities.
Danielle is most proud of building long term relationships and creating investment strategies with her clients. She is passionate about assisting new investors of any age to create wealth and passive income by building their real estate portfolio as well as working with seasoned investors to procure additional investments, manage and add value to their current real estate investments.
Danielle loves living by the beach in Belmont Shore and spends her free time with family, traveling and exploring with her twins. However, her commitment and passion to serving her clients equals real opportunities so reach out to her today to discuss how she can assist you in creating your success story to retire early.
1. INDUSTRIAL’S LARGEST OPERATORS EXPAND
- According to an article by Commercial Observer, Industrial real estate heavyweights Prologis and Link Logistics are leading an ongoing expansion in warehouse use despite recent reports of a post-COVID-boom slow in demand.
- Industrial real estate demand has softened in recent months but has retracted from record double-digit growth experienced in 2022 and early 2023. E-commerce’s share of retail sales remains in a new post-pandemic paradigm, and while near-term growth may slow, operators with ample liquidity and a long-term eye remain active in the current environment.
- The CEOs of both companies indicated that they expect to add similar or higher leasing volume in 2024 compared to last year. Link Logistics added 86 million square feet of leased space in 2023, including 23 million in the fourth quarter. Prologis is looking to add up to $3.5 billion in new development in 2023 and expects occupancy levels to remain at or above 96%.
2. HOMEBUILDER SENTIMENT RISES
- Based on data from the NAHB/Wells Fargo Housing Market Index, homebuilder sentiment about housing market sales conditions rose to its highest level in eight months.
- The index measuring views of current sales conditions rose four points to 56. Conditions have steadily rebounded since reaching a recent nadir of 24 in November 2023. Index measures above 50 indicate positive sentiment.
- Expected sales conditions over the next six months also increased, climbing two points to 62. Prospective buyers’ traffic rose similarly two points to 34.
- NAHB economist Robert Dietz mentions that as potential rate cuts stimulate demand, rising material prices, particularly lumber, will impact homebuilder activity. Rising activity could also impact logistics and warehouse inventories as market intermediaries ramp up to meet demand.
3. MIXED-USE PROPERTIES
- As trouble in the Office sector causes some investors to consider repositioning their portfolios, mixed- used projects are emerging as a prospective choice for developers.
- Mixed-use projects bring together office, retail, and residential spaces and offer a medium for reimaging at-risk sub-sectors like indoor shopping malls and CBD office spaces.
- Jamestown, a real estate developer, has utilized the mixed-use approach to implement ambitious projects that accommodate varied local market environments, such as in Atlanta, Brooklyn, and Raleigh.
- Mixed-use projects also offer developers a way to test the success of newer and emerging product types such as advanced manufacturing, life sciences, flex-living, and health and wellness alongside more tried and tested concepts such as traditional residential and retail space.
4. COASTAL PROPERTY VALUES DEFY CLIMATE RISKS
- Despite risks from sea-level rise and storms, US coastal communities remain a hotspot for growth as high-income residents continue to purchase in and populate these areas.
- Coastal property values continue to climb, with both market and policy forces appearing to be at play. A recent study by Nature found that a combination of stable property values for investment, tax advantages for high-income owners, and subsidies for coastal management activities such as beach nourishment have dampened the effect of sea-level rise on coastal property values.
- Still, the report cautions that such effects are likely temporary and that policy components, such as subsidies and tax advantages, distort the price signals that typically reflect longer-term risks.
5. COMMERCIAL PROPERTY PRICES
- According to the MSCI-RCA commercial property price index (CPPI), the decline in US commercial sector prices slowed further in February, declining just 4.0% year-over-year.
- Price declines in CRE have been consistent over the past year and a half, but in February, they fell at their slowest pace of annual decline since 2022 and dropped just 0.3% month over month.
- The industrial sector again emerged as the only property type with an annual increase, growing by 1.9% year over year and 0.2% month over month.
- Apartment sector prices declined 8.9 % year-over-year but extended a six-month-long moderation in annual price declines for multifamily properties. Still, apartment prices posted the largest month-over-month decline across all sectors, falling 0.1%.
- Retail sector prices were flat month-over-month, but annual returns fell by 2.5%. Notably, annual price declines in the sector have softened from the double-digit declines seen during the third quarter of 2023.
- Suburban office prices fell 11.6% year over year and 0.4% month over month. Meanwhile, CBD office valuations fell 29.9% annually and 1.3% monthly. The differing magnitudes of devaluation largely reflect each subtype’s sensitivity to remote work. The negative demand shock appears most intense in dense, high-price office markets.
6. FED INTEREST RATE DECISION
- The Federal Reserve held interest rates steady at its March policy meeting, in line with market expectations that policymakers would continue its wait-and-see approach for the time being.
- Both the Fed and fed futures markets, as indicated by the Chicago Mercantile Exchange’s Fed Watch Tool, kept consistent their projections of three rate cuts by the end of 2024.
- Inflation has come down consistently over the past year, but resilient labor market and consumer spending dynamics have kept price pressures salient and inflation expectations elevated.
- In his post-meeting statement, Fed Chair Jerome Powell stated that the committee is prepared to maintain current interest levels for longer if needed to re-anchor price stability and expectations.
7. CORPORATE TO CRE DEBT SPREAD HITS 24-YEAR HIGH
- Based on data from MSCI, a snapshot of US capital markets shows that the spread between corporate versus commercial real estate debt rates has risen to a high of at least 24 years.
- Dating back to 2000, mortgage rates were consistently low relative to the cost of corporate debt except for during the worst parts of the Great Financial Crisis (GFC), according to the MSCI analysis.
- The rising relative cost of CRE debt indicates that investors are recalibrating the sector’s risk profile relative to other investments. Higher interest rates impact investor returns, with investment funds feeling the pinch recently, according to the report.
8. CRE TOP RISK, SAYS UBS
- UBS recently flagged a potential commercial real estate downturn as a “top and emerging risk” that it’s preparing for in 2024. It cited higher borrowing costs and slumping demand as potential headwinds in its outlook.
- In its annual 2023 report, UBS noted that “adverse effects on valuations from higher interest rates” and a “structural decline in demand for office and retail” could trigger impacts on the bank, given its exposure to the sector.
- UBS’s citing of CRE risks does not suggest a significant CRE downturn. Still, it indicates how shifting supply and demand dynamics may affect the balance sheets of financial firms invested in at-risk assets. The broader CRE market remains a story of diverging sector-level performance and varied metro-area trends.
9. CONTEXTUALIZING CRE RISKS TO BANKS
- According to a recent report by Cohen and Steers, CRE risks to the banking system are spread across large, mid, and small-sized institutions, significantly mitigating potential risks to the financial system.
- The top 25 largest US banks by total assets hold 13% of all commercial real estate mortgages but have just 4% of their total assets exposed to the sector.
- Regional and community (mid-sized) banks are more exposed relative to the market as they hold roughly 30% of all CRE mortgages and, on average, have a 20% balance sheet exposure.
- Banks outside of the top 100 account for roughly 15-20% of all CRE mortgages, but exposure is spread across more than 4,500 institutions nationally.
- Further, their debt service coverage ratios indicate that loan term default risks and low and underwritten values on existing loans are low, as property values have risen over the past ten years.
10. NAR SETTLEMENT
- A recent landmark settlement between the National Association of Realtors and consumer advocates reforms how brokers can charge commissions on home sales, eliminating the standard 5-6% fees charged to sellers to have their homes posted on Multiple Listing Services (MLS).
- If approved, the settlement would open MLS sites to negotiated pricing, and changes to the brokerage fee structure would take effect within months of approval. A hearing on whether to approve the deal is set to take place in the next few weeks.
- Advocates of changes to the system point out that the settlement could increase price transparency and competition in the home-selling industry.
SUMMARY OF SOURCES
- (1) https://commercialobserver.com/2024/03/industrial-real-estate-more-inventory-2024/
- (2) https://www.nahb.org/news-and-economics/housing-economics/indices/housing-market-index
- (3) https://www.globest.com/2024/03/27/mixed-use-much-more-than-office-retail-residential/
- (4) https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-46548-6
- (5) https://www.msci.com/our-solutions/real-assets/real-capital-analytics
- (6) https://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/pressreleases/monetary20240320a.htm
- (7) https://www.globest.com/2024/03/27/spread-between-corporate-debt-and-cre-mortgages-hits-24-year-high/
- (8) https://www.reuters.com/markets/europe/ubs-flags-commercial-real-estate-downturn-top-risk-2024-03-28/
- (9) https://www.cohenandsteers.com/insights/the-commercial-real-estate-debt-market-separating-fact-from-fiction/
- (10) https://www.nbcnews.com/business/consumer/realtor-settlement-affects-homebuyers-sellers-how-explainer-rcna144650


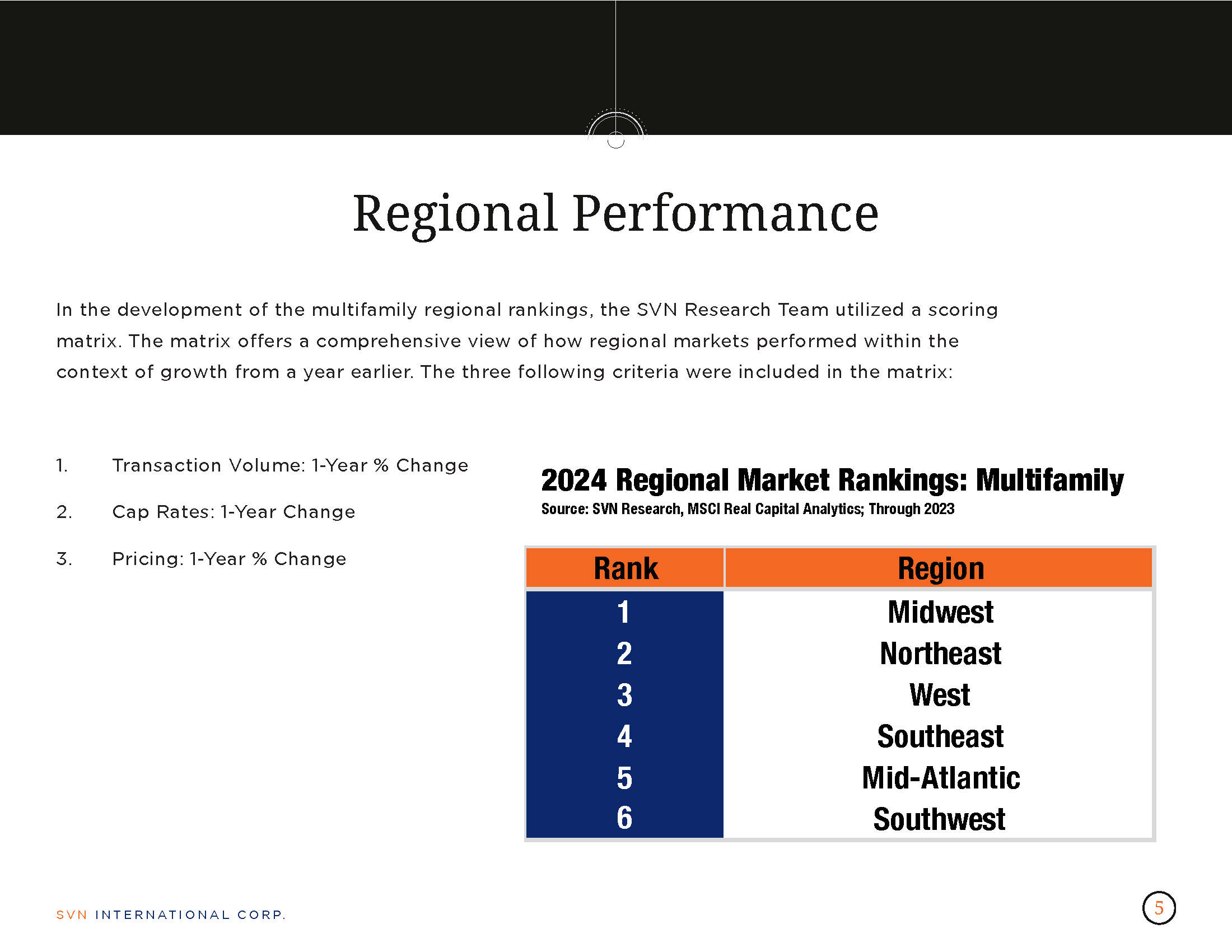


The SVN Regional Office was also named #3 in the nation among all SVN brokerages for 2023.

SVN Vanguard finished #1 in the region and #3 nationally in this year’s SVN National conference in Miami, FL. Following a successful 2022 campaign as the international firm of the year, SVN Vanguard continues to deliver top tier performance for 2023.
In addition, the San Diego County Vista Chamber of Commerce named the SVN | Vanguard North County Office the New Business of the Year.
To compile rankings for SVN’s national conference, SVN International Corp. identifies the top producing brokerages and advisors based upon closed commercial real estate transactions. Top producing Advisors are ranked in three different categories based on their gross commission income (GCI). The categories are: Partner’s Circle, President’s Circle and Achiever Award. Tony Yousif, Director- National Accounts, achieved Partner’s Circle status as one of the top advisors in the SVN network. Cameron Irons, Executive Director at SVN Vanguard, and Senior Vice President, Jon Davis, were also recognized for ranking within the Top 100 Advisors of 2023.
About SVN Vanguard
SVN Vanguard is a full-service commercial real estate office of the SVN brand, comprising over 1,600 commercial real estate Advisors and staff, in more offices in the United States than any other commercial real estate firm and continues to expand across the globe. We believe geographical coverage and amplified outreach to traditional, cross-market and emerging buyers and tenants is the only way to achieve maximum value to our clients. Visit http://www.svnvanguardoc.com for more information.






SHAREABLE FLIPBOOK DOWNLOADABLE PDF
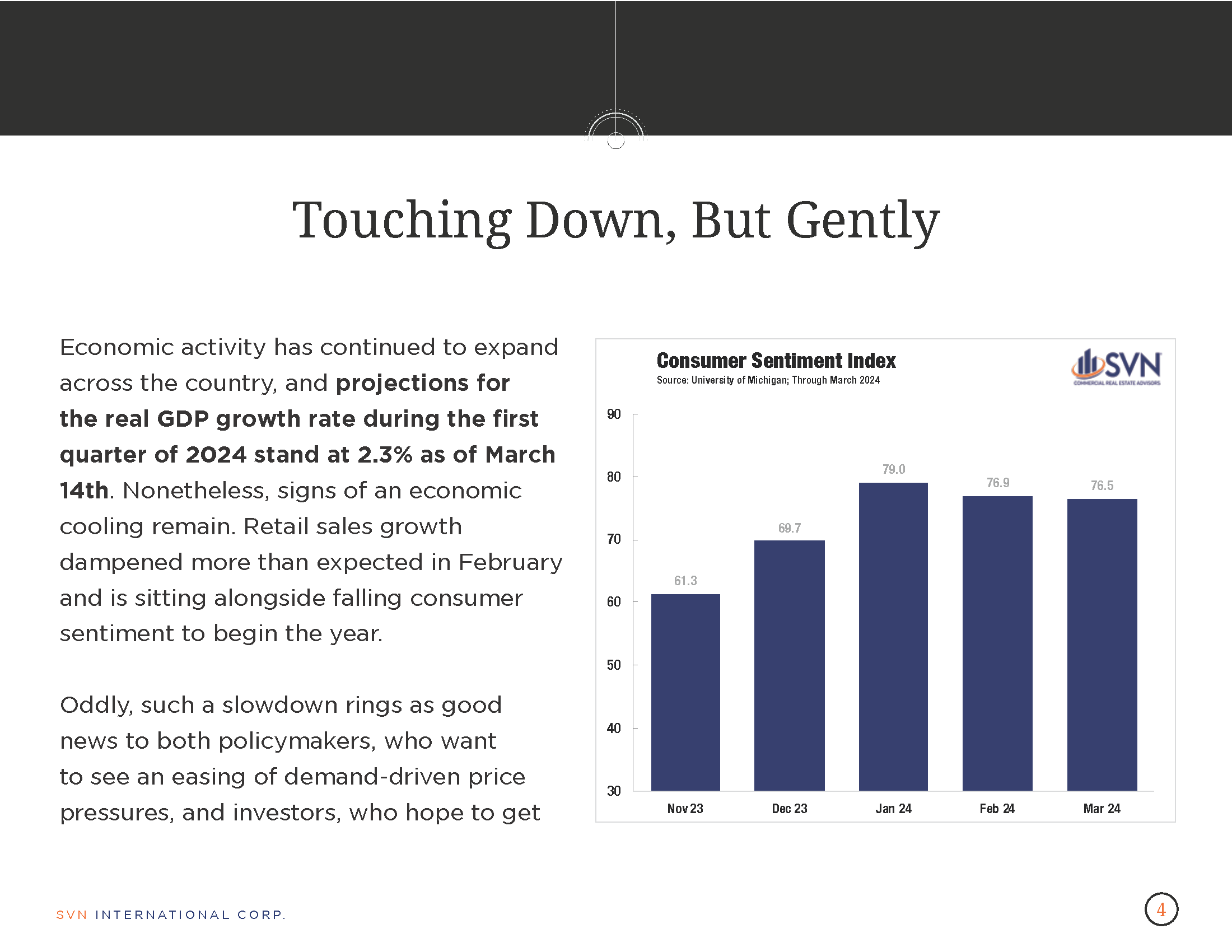
1. INFLATION
- According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the Consumer Price Index rose 0.3% month over month in January and 3.1% annually.
- The monthly pace of CPI rose above market expectations and triggered a brief reversal in equity markets. Fed officials have also been increasingly warning against a premature judgment on the path of its interest rate policy, given the volatility in inflation data and the myriad factors at play.
- The shelter index continued to climb in January, rising 0.6% on the month and contributing more than two-thirds of the monthly increase.
- US energy prices fell -0.9% on the month, bringing the total price change over the previous 12 months to -4.6%. Meanwhile, food prices increased by 0.4% month-over-month in January, driven by both food-at-home and food-away-from-home prices.
- Core-cpi prices, which exclude food and energy, rose 0.4% in January.
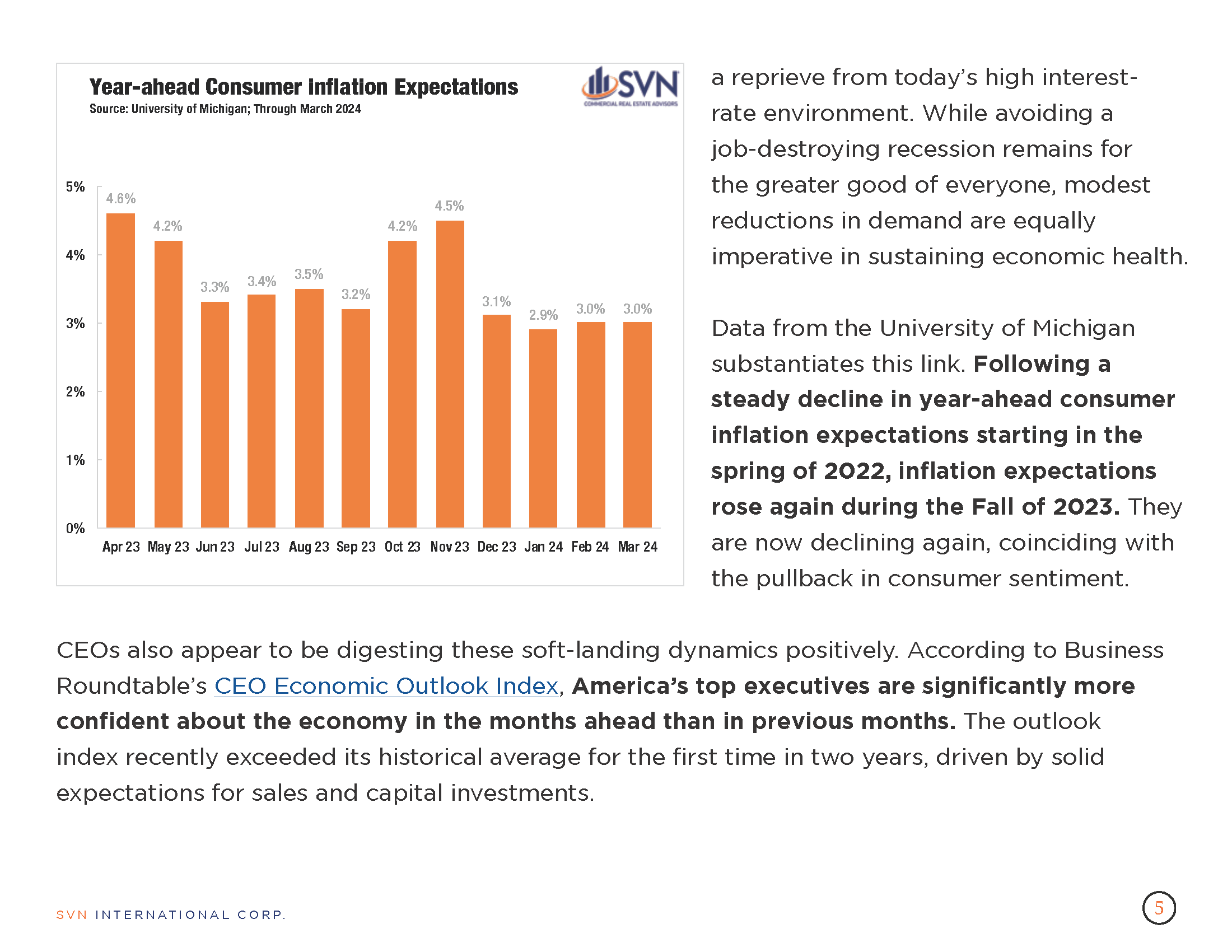
2. FOMC MINUTES
- FOMC officials continue to express caution about cutting rates prematurely as the economic picture for 2024 continues to be beset by uncertainties, minutes from their most recent policy meeting show.
- At their January meeting, the FOMC held rates unchanged as they await further inflation and labor market developments. Notably, their post-meeting statement included updated language surrounding the path of rate cuts, with officials reiterating that no cuts would occur until the committee held “greater confidence” that inflation was receding.
- The January tally of CPI justifies the committee’s caution, as price pressures registered higher than markets had expected and initiated a brief price correction in the stock market.
- However, the minutes reflect a general sense of optimism by officials that the policy moves they pursued over the past two years have been successful. Inflation reached a 40-year high in 2022 and has steadily come down since.
3. RACIAL INEQUITIES IN US HOUSING
- According to the 2024 Chandan Economics Racial Inequities in US Housing Report, emerging challenges in housing affordability and credit conditions display disproportional impacts across racial groups.
- Housing affordability indices have fallen precipitously over the past two years, placing further constraints on renter incomes. As of Q4 2022 (the latest data available), 22.5% of all renter households live at or below the poverty line.
- Moreover, constraints show wide variations by racial groups. 37% of Native American or Alaskan Native renter households and 30% of Black renter households fall at or below the poverty line. 25% of Hispanic renter households of all ethnicities and 21.6% of households identifying as multi-racial meet this threshold. The rate falls for White and Asian renter households to 19.9% and 19.4% respectively.
- As borrowing costs and American consumer debt levels rise, credit health and access exhibit similar racial disparities. According to an analysis by Oliver Wyman, on average, 45% of Americans receive prime credit rates. When measured by race, 62% of Asian Americans, 51% of White Americans, 29% of Hispanic Americans, 24% of Americans of other racial groups, and 20% of Black Americans receive prime credit rates.
4. CRE DELINQUENCIES OUTPACE RESERVES
- A recent analysis by the Financial Times reports that the level of delinquent commercial real estate debt held by the largest big banks surpassed their total bank reserves in 2023, raising concerns about the financial system’s exposure to emerging risks.
- Utilizing data from the FDIC, the report found that the average reserves at the nation’s largest six banks have fallen from $1.60 to 90 cents for every dollar of CRE debt on which a borrower is at least 30 days late.
- Bank reserves are used to buffer against potential loan losses, and as real estate valuations fall alongside rising interest rates, pressure on reserves has increased.
- Still, it is essential to note that delinquencies don’t mean defaults, and the immediate concern for regulators is the banks’ exposure to potential risks rather than a judgment of loan conditions.
- Last year, the Federal Reserve’s supervisory functions refocused efforts toward banks and their exposure to interest rate and CRE risk following a string of bank failures during the first half of the year. Officials have increased the issuance of enforcement actions and downgrades in an effort to deter complacency.
5. PENSION INVESTMENTS IN CRE FALL
- A report by Ferguson Partners details how investment pledges to commercial real estate funding vehicles from US pensions fell by 50% in 2023 to its lowest commitment level in a decade.
- Momentum began to slow during the second half of 2023, while the 2023 average fell 25% below the average volume of the last ten years. Analysts from Ferguson call the development a “stark recalibration” from the upward trend seen over the previous five years.
- Industrial property funds attracted the largest share of CRE pledges (35%), followed by those targeting data centers, life sciences, and SFR (33%), and multifamily (27%).
6. HOMEBUILDER SENTIMENT
- According to the National Association of Home Builders, builder sentiment improved for a third consecutive month in January as construction firms expect mortgage rates to continue to moderate from last year’s levels.
- The prospect of a Fed pivot to rate cuts in 2024, alongside a lingering lack of housing supply, suggests that all else equal, building activity should improve in the coming months. However, in recent days, higher-than-expected inflation data and cautionary signals by Fed officials have pushed markets to reconsider their rate-cut expectations for 2024.
- NAHB forecasters project that at current conditions, any Fed-rate cut would likely come in the latter half of 2024, which would send single-family starts up by 5% compared to 2023, based on their forecasting.
- NAHB Economists note, however, that as building activity rises, lot availability and a shortage of skilled labor will become a growing concern.
7. “AGING IN PLACE” AND THE US HOUSING SHORTAGE
- A new analysis by Redfin shows that an increasing number of older Americans are “aging in place,” meaning they increasingly remain in their established homes rather than downsizing or moving to senior communities. The trend may complicate an already stubborn US housing shortage.
- The average US homeowner of all ages has spent 11.9 years in their home, almost double the average of 6.5 years two decades ago.
- Tenure peaked in 2020 as the pandemic homebuying boom induced a moderate decline in the rate. However, much of this downtrend was driven by millennials buying their first homes or being more inclined to initiate a life change.
- Meanwhile, baby boomers continue to stay in their homes for longer. As homebuying cools relative to pandemic-era highs, the trend in tenure may again inflect.
- Part of the reason behind the trend is financial. Most baby boomers own their homes free and clear, and longer-tenured owners bought mortgages at much lower rates than today’s generationally high rates. Further, some states retain tax incentives for older homeowners, including two of the most populated— Texas and California.
- Non-financial reasons, including generational views on assisted living and advancements in medical and tech, have also recalibrated senior housing demand.
8. BUSINESS OPTIMISM
- According to the National Federation of Independent Businesses (NFIB), small businesses grew more pessimistic in January, with the index tracked by NFIB falling to 89.9, its lowest level in eight months.
- Labor quality and inflation remained the top concerns for business owners. 21% of owners reported labor quality as their single most important problem in operating their business, while 20% cited inflation as their top problem.
- Interestingly, as a sign of improving hiring conditions, the share of owners reporting job openings they can not fill fell to 39%, the lowest reading since January 2021.
- However, hiring plans are also at a post-pandemic low. Only 14% of owners intend to create new positions within the next three months, down two percentage points from December and its lowest since May 2020.
9. COMMERCIAL PROPERTY PRICES
- According to the MSCI-RCA commercial property price index (CPPI), the decline in US commercial sector prices slowed further to start 2024.
- Prices fell 4.7% year-over-year through January but just 0.1% from December. For context, the commercial sector saw annual price declines of around 11% during the summer of 2023.
- The industrial sector again arose as the only property type with an annual increase in January. The average price on an Industrial property climbed 1.2% month-over-month from December and 1.3% over the past 12 months. The Industrial sector has experienced consecutive monthly price increases since June 2023
- Apartment sector prices declined 7.9% year-over-year, an improvement over the past several months as markets increasingly expect a Fed policy pivot on the horizon. Apartment price declines peaked in August of last year when they fell at an annual rate of 14.1%.
- Retail joined Industrial as the only sectors to post monthly price increases in January. Retail sector prices rose 0.1% from December following a -0.1 decline in the previous month. Sector prices fell -3.6% year over year, an improvement over December’s -5.5% and the sixth consecutive month of improvement.
- Suburban office prices fell -11.9% year-over-year and -0.4% month-over-month. Meanwhile, CBD office valuations fell -28.9% annually but saw its rate of monthly decline slow to just -1.0%. The differing magnitudes of devaluation largely reflect each sub-type’s sensitivity to remote work. Simply put, the negative demand shock appears most intense in dense, high-price office markets.
10. RETAIL SALES & INVENTORIES
- According to data from the US Census Bureau, US retail sales rose 0.6% year-over-year in January, the slowest pace of annual growth since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Sales were down 0.8% from December.
- While sales growth has come back down to earth after achieving a record high of 52.0% year-over-year in April 2021, the industry appeared to hit a nadir of 1.29% in April 2023 and has grown steadily since then. January’s 0.6% annual mark challenges this trend and is a steep drop from the 5.31% charted in December.
- A seasonal pull-back in activity is expected during January and February as the holiday boom in sales cools off.
- Automobiles and vehicle parts continue to outperform the broader retail market. Excluding autos, US retail sales declined 0.6% month-over-month in January and climbed 1.2% year-over-year.
- Directional movement in sentiment than non-investors.
SUMMARY OF SOURCES
- (1) https://www.bls.gov/news.release/cpi.nr0.htm
- (2) https://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/pressreleases/monetary20240221a.htm
- (3) https://www.chandan.com/_files/ugd/df56fe_07f73f4b0a054d35b4d578e36afda4f7.pdf?index=true&utm_campaign=4cd7dbe2-1a0a-4402-80e8-02dc3fc1ac51&utm_source=so&utm_medium=mail
- (4)https://www.ft.com/content/4114454c-a924-4929-85f4-5360b2b871c6
- (5) https://www.globest.com/2024/02/21/cre-pledges-from-us-pensions-drop-50/
- (6) https://www.nahb.org/news-and-economics/press-releases/2024/02/builder-sentiment-posts-third-consecutive-monthly-gain
- (7) https://www.redfin.com/news/homeowner-tenure-2023/
- (8) https://www.nfib.com/
- (9) https://info.msci.com/l/36252/2024-02-21/y1htr4/36252/1708559067qvvmBG37/2402_RCACPPI_US.pdf
- (10) https://www.census.gov/retail/marts/www/marts_current.pdfx
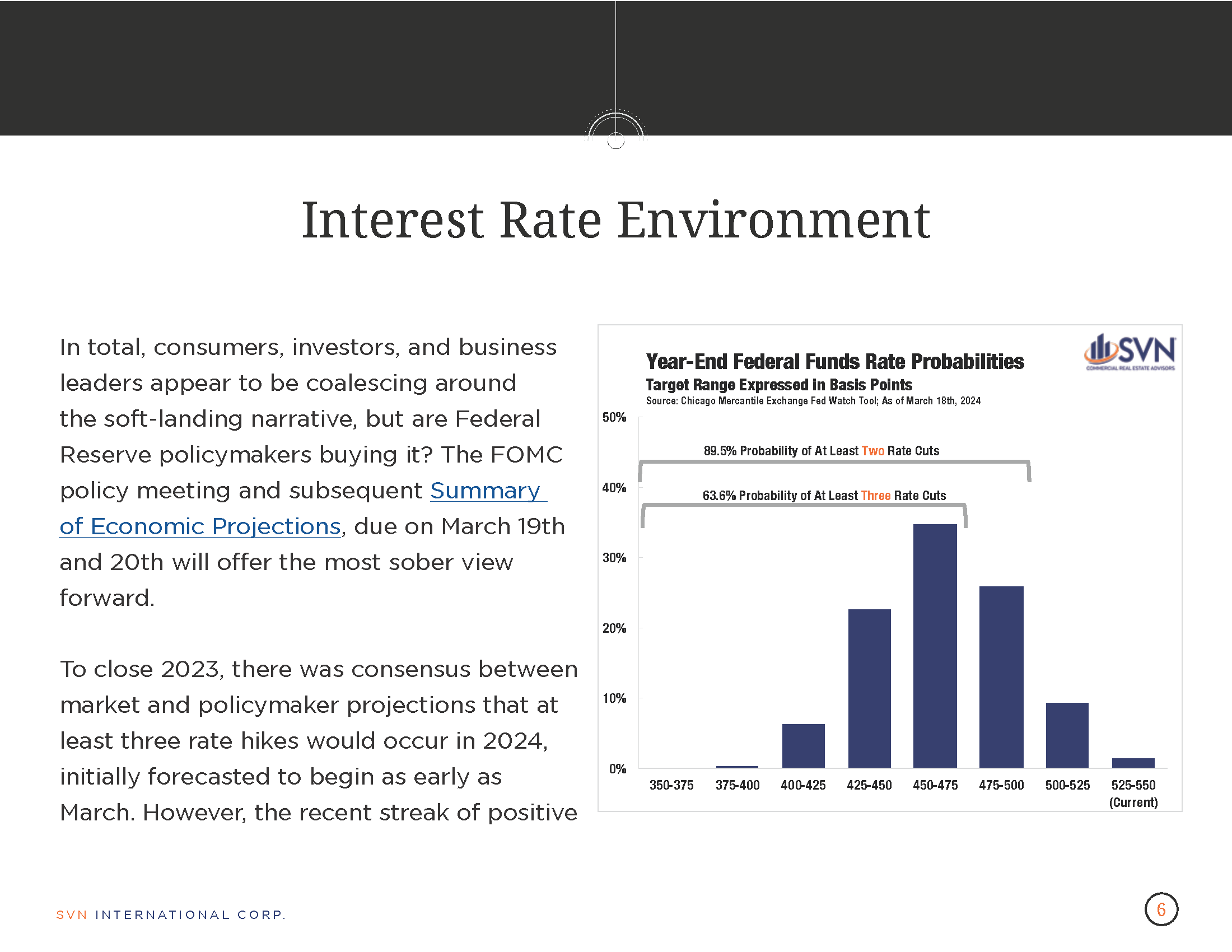
Along with all other loan kinds, lenders anticipate a rise in demand for CRE loans as well.
In order to have a deeper understanding of banks’ lending practices, the Federal Reserve conducts frequent checks with them through the Senior Loan Officer Opinion Survey on Bank Lending Practices (SLOOS). The most current survey’s short summary for commercial real estate is that increasingly stricter underwriting requirements should be anticipated in the future.
Furthermore, although relatively modest demand from borrowers is eventually anticipated to be supported by softening interest rates, that is unlikely to occur until May or June.
The research stated that during the fourth quarter, a considerable number of banks reported tightening their rules for all kinds of CRE loans. Tightening requirements, particularly by the “other banks” group, were also true for multifamily loans. “Such tightening was more widely reported by other banks [or those with less than $50 billion in assets] than by large banks.”
A substantial net share of banks reported weaker demand for construction and land development loans, and major net shares of banks reported weaker demand for loans secured by nonfarm, nonresidential, and multifamily residential properties, they continued. Over the course of the fourth quarter, notable net shares of foreign banks reported tighter standards and a decline in the demand for CRE loans.
The percentage of respondents who are tightening conditions for CRE loans is close to the 2009 peak of the global financial crisis and just below the peak of the 2020 pandemic. Furthermore, the percentage of domestic respondents who reported a higher demand for CRE loans is significantly lower than it was during the GFC.
Banks expect demand for loans to increase as interest rates decrease, but with Fed messaging, this is unlikely to happen until May or June at the earliest. Dave Sloan, a senior economist at Continuum Economics, told Reuters that the results are “unlikely to generate any urgency for easing.”
An expected decline in collateral values, a less favorable economic outlook, an expected decline in the credit quality of the bank’s loan portfolio, an expected reduction in risk tolerance, an expected decline in the bank’s liquidity position, and increased concerns about funding costs and the effects of legislative or regulatory changes were the most commonly cited reasons for expecting to tighten lending standards over 2024, according to major net shares of banks, the Federal Reserve stated.
In layman’s words, the problem is bank anxiety, which has persisted since the early 2023 closures of First Republic Bank, Silicon Valley Bank, and Signature Bank. The shares of New York City Bancorp, which acquired the majority of Signature’s assets, including its CRE loan portfolio, have continued to tumble for almost a week now. At the closing on February 6, shares had dropped about 60%, from roughly $10.30 to $4.20.
There were other issues plaguing the New York community than just Signature. Though they were all tied to commercial real estate, there was also an additional charge-off on an office loan that went non-accrual during the third quarter, based on an updated valuation, and a New York cooperative loan that wasn’t in default but is now up for sale due to a unique feature that pre-financed capital expenditures. Furthermore, if one bank trembles, so do many more.
We are ready to assist investors with Santa Ana Commercial Real Estate properties. For questions about Commercial Real Estate Investments, contact your Orange County commercial real estate advisors at SVN Vanguard.































